

Best Life Fertility Center
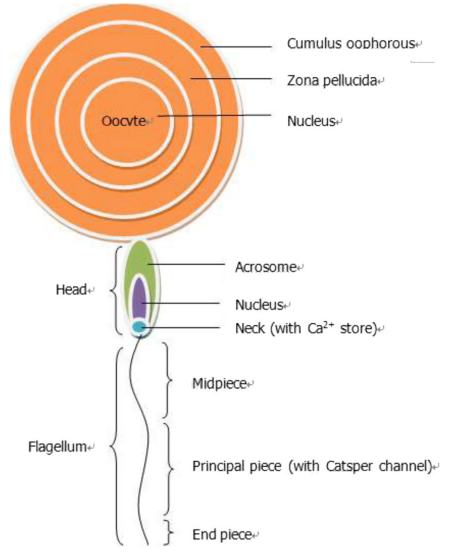
The Catsper channel is a unique, sperm-specific calcium ion channel essential for sperm function. It is located in the tail of the sperm and controls calcium entry, which is crucial for sperm motility, hyperactivation (the vigorous swimming motion needed to reach the egg), and the ability to fertilize. Unlike other calcium channels in the body, Catsper is found only in sperm cells.

©2025 Bestivf.ae All Rights Reserved.
Powered by Cielo Creatives
WhatsApp us